ELECTROPOLISHING
Electropolishing, also known as electrochemical polishing or electrolytic polishing (especially in the metallography field), is an electrochemical process that removes material from a metallic work piece. It is used to polish, passivate, and deburr metal parts. It is often described as the reverse of electroplating. It may be used in lieu of abrasive fine polishing in microstructural preparation.
Electropolishing has many applications in the metal finishing industry because of its simplicity and it can be applied to objects of complex shape. Typical examples are electropolished stainless steel drums of washing machines and stainless steel surgical devices. Electropolishing is also commonly applied to the preparation of thin metal samples for transmission electron microscopy because electropolishing does not cause mechanical deformation of surface layers usually observed when mechanical polishing is used. Ultra high vacuum (UHV) components are typically electropolished in order to have a smoother surface for improved vacuum pressures, outgassing rates, and pumping speed.
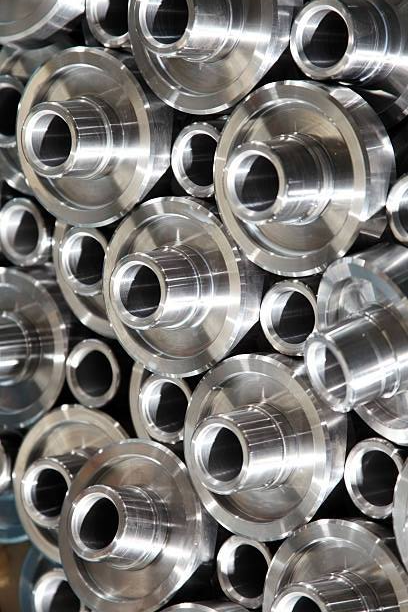

BENEFITS OF ELECTROPOLISHING INCLUDE:
Removes iron from the surface and enhances the chromium/ nickel content providing the most superior form of passivation for stainless steel.
- Provides a clean and smooth surface that is easier to sterilize.
- Polishes areas inaccessible by other polishing methods.
- Improves the surface finish by leveling micro peaks and valleys.
- Removes a small amount of material from the surface of the parts, also removing small burrs.
- Can be used to reduce the size of some parts when necessary.
- Results are seen by many as aesthetically-pleasing.







 323-268-6353
323-268-6353









 323-268-6353
323-268-6353